Modern physical therapy techniques used at the Center for Brain Stimulation help ensure effective treatment with positive results as early as the first day of treatment and minimize the risk of health-threatening complications.

Kiev

Addresses of the Clinics
+38 (073) 073-03-85 +38 (096) 665-57-97 +38 (099) 353-91-84
Monday-Sunday 08:30 - 20:00
Modern physical therapy techniques used at the Center for Brain Stimulation help ensure effective treatment with positive results as early as the first day of treatment and minimize the risk of health-threatening complications.

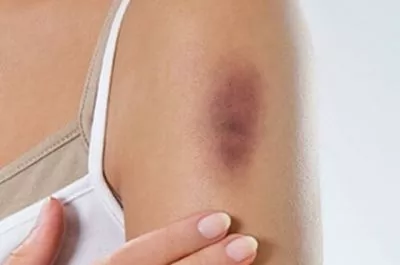
A hematoma is a limited accumulation of blood in closed and open injuries of organs and tissues with ruptured blood vessels. A hematoma forms a cavity that contains blood.
Normally, a hematoma is harmless, but sometimes, if it is large, the hematoma must be removed. Especially if there is a risk that it could affect the function of neighboring organs and tissues.
Modern physiotherapy techniques used at the Center for Brain Stimulation help ensure effective treatment with positive results from the first day of treatment and minimize the risk of health-threatening complications.
There are several classifications of hematomas. As with other medical problems, they are based on the main features:
In addition, hematomas are subcutaneous, intratissue, and intracranial.
A subcutaneous hematoma is an accumulation of liquid or coagulated blood in the hypodermis. The main signs of a hematoma under the skin are bruising and signs of fluid accumulation under the skin (confirmed by opening the hematoma or by ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging).
Intramuscular (intrathecal) hematoma differs from subcutaneous hematoma in the depth of placement - blood saturation of the tissue and edema are in deeper layers, therefore acupressure diagnosis and visual examination become less effective.
Intracranial hematoma is a hemorrhage in the cranial cavity. In turn, it is subdivided into traumatic intracerebral hematoma, acute traumatic subdural hematoma, and epidural hematoma.
Causes of hematoma are usually associated with trauma preceding the problem. Most often, the cause of a hematoma is indeed post-traumatic internal bleeding, which can result from impact, compression, impingement, and other trauma. But along with this, a hematoma can also be caused by non-traumatic damage to the integrity of the vessel walls. Also, hemorrhages can occur with some internal organ hemorrhages.
Hematomas can form in injuries of any type, in any part of the human body and in all types of injuries (open, closed).
The main symptoms of a hematoma located in the subcutaneous tissue and muscles, which help distinguish it from an ordinary superficial bruise:
As a rule, the symptomatology and severity of extracerebral hematomas depends on the location and size of the hematoma, as well as the degree of compression of the surrounding tissues.
When internal organs are injured, the main symptom of a hematoma that you should definitely pay attention to is compression of the organs.
A hematoma inside the skull may show the following signs:
If any of the above signs occur, it is necessary to seek medical attention immediately. Specialists include a trauma surgeon and a neurologist.
Statistically, a retrochorial hematoma occurs in approximately 25% of pregnant women. This is the most common pathology that is detected by the ultrasound technician when examining a pregnant woman with an ultrasound machine. Usually such a hemorrhage is small and spontaneously resolves itself and is not harmful to the health of either the expectant mother or the child. The most dangerous is a hematoma during pregnancy in the III trimester. It can be a symptom/consequence of placenta previa or placenta detachment, which requires urgent intervention.
One of the most dangerous complications of a soft tissue hematoma is suppuration with further abscess formation. Most often, this problem occurs with a concomitant skin lesion, in which infectious agents enter the cavity. In such an unnatural process, there is an increase in pain, local hyperemia, and signs of general intoxication.
In severe and neglected cases, the purulent process spreads - the formation of phlegmon and the development of sepsis are possible. Whatever the consequences of a hematoma, they are unpleasant. Therefore, if you have such a problem, immediately seek qualified help. At the Center for Brain Stimulation you will be treated quickly, qualitatively, without bringing the process to the point where the situation can only be helped by the removal of the hematoma.
Most hematomas (subcutaneous and intramuscular types) do not require instrumental or laboratory diagnosis: diagnosis is made on the basis of evaluation of the lesion site, symptoms and palpation. If there is an urgent need, a detailed blood test and a coagulation test are prescribed. Instrumental methods - ultrasound and CT scanning - are used to diagnose hematomas, which may appear after internal hemorrhages, their timely detection and taking measures.
Don't know what to do if you have a hematoma? Contact us.
There are plenty of first aid remedies for subcutaneous and intramuscular hematomas - rest, cold and/or pressure dressings, ointments for hematomas from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and anticoagulants, other. Even more folk remedies. But, the most effective remedy offered by the Center for Brain Stimulation is the treatment of hematoma with the help of physiotherapeutic methods. For this purpose our clinic widely uses high-intensity magnetic therapy, which shows positive results already after 1 session. This type of physiotherapy on the Super Inductive System, is observed by our doctors, who have extensive experience in treating hematomas, qualitatively improves the circulation and trophicity, and has an analgesic effect.
Hematomas developed in the abdominal cavity or inside the skull are treated differently depending on their size and the degree of deterioration of body functions: in some cases the therapy is limited to observation of the patient, while in other cases surgical intervention and inpatient treatment are applied.
The key preventive measure of hematoma is to avoid injuries, take care of your immune system and blood clotting levels.
Do you ask a question, "Which doctor does treat hematomas?" - contact our call-center, here you will be explained who to contact, how to make an appointment, and select a convenient time for your visit. Hematoma treatment at the Center for Brain Stimulation is medical services for the diagnosis and treatment of different types of this problem. With us you get:
Sign up for a course of high-intensity magnetic therapy and see the result after the first session!
Ирина 23.06.2021
Лечение гематомы
У меня хрупкие сосуды, поэтому гематомы у меня очень частые гости. Обратилась в ЦСМ, чтобы подлечить сосуды и пройти курс физиотерапевтических процедур. Анализ крови показал низкий уровень свертываемости. Буду принимать медикаменты, соблюдать диету. Уровень клиники очень достойный.
Юрій Борисович 13.05.2021
Лікування гематоми
Дуже сильний удар по нозі викликав найсильніший синяк, добре, що не перелом. У мене путівка на відпочинок в Єгипет, як мені їхати з хворою та ще й страшною ногою. Пішов до реабілітолога Паламарчука С. А. Робили магнітотерапію всього три рази, на більше не було часу. Але біль пройшов і колір став вже жовто-зеленим, так що можна і на курорт.
Юля Онищенко 04.04.2021
Лечение гематомы
Очень неприятная ситуация у меня вышла с массажистом. Антицеллюлитный баночный массаж закончился для меня сплошным синяком! До свадьбы осталось полторы недели, платье открытое. А у меня гематомы как от побоев. УЖАС!!! Хорошо подружка порекомендовала классные процедуры в ЦСМ. Магнитотерапия длилась 10 минут, но боль после одного сеанса стала в два раза меньше! Я в восторге! За несколько сеансов я буду снова красавица!